[Java] 스레드 풀이란?
java-study에서 스터디를 진행하고 있습니다.
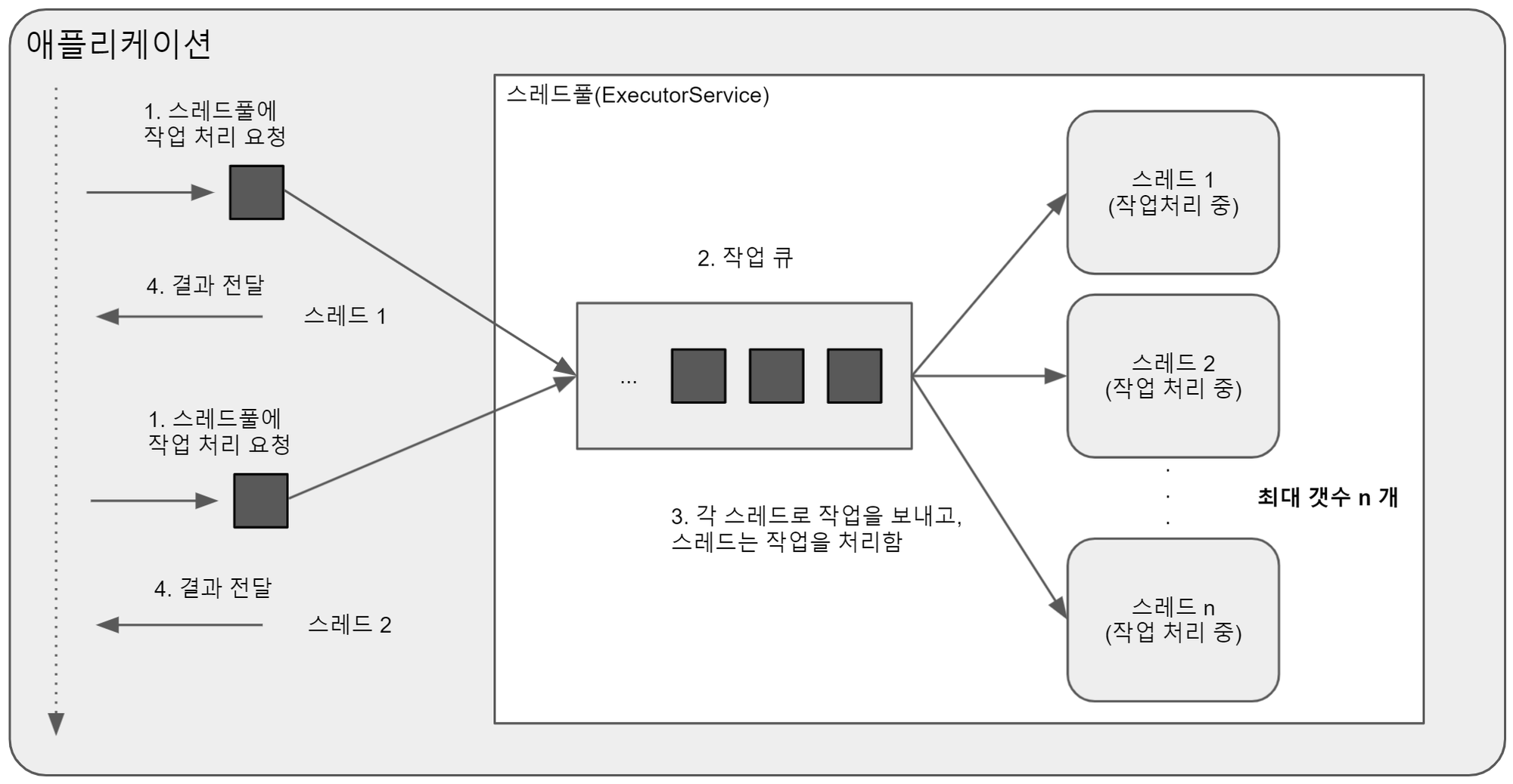
스레드 풀 개념
- 병렬 작업 처리가 많아지면 스레드 개수가 중가되고, 그에 따른 스레드 생성과 스케줄링으로 인해 CPU가 바빠져 메모리 사용량이 늘어난다. 이는 애플리케이션의 성능 저하로 이어진다.
- 병렬 작업의 폭증으로 인한 스레드의 폭증을 막으려면 스레드 풀을 사용해야 한다.
- 스레드 풀은 작업 처리에 사용되는 스레드를 제한된 개수만큼 정해 놓고 작업 큐에 들어오는 작업들을 하나씩 스레드가 맡아 처리한다.
- 작업 처리가 끝난 스레드는 다시 작업 큐에서 새로운 작업을 가져와 처리한다.
- 따라서 작업 처리 요청이 폭증해도 작업 큐라는 곳에 작업이 대기하다가 여유가 있는 스레드가 그것을 처리하므로 스레드의 전체 개수는 일정하며 애플리케이션의 성능도 저하되지 않는다.
스레드 풀 생성 및 종료
자바는 스레드 풀을 생성하고 사용할 수 있도록 java.util.concurrent 패키지에서 ExecutorService 인터페이스와 Executors 클래스를 제공한다.
스레드 풀 생성
ExecutorService 구현 객체는 Executors 클래스의 다음 두 가지 메소드 중 하나를 이용해서 간편하게 생성할 수 있다.

- 초기 스레드 수: ExecutorService 객체가 사용될 때 기본적으로 생성되는 스레드 수
- 코어 스레드 수: 스레드 수가 증가된 후 사용되지 않는 스레드를 스레드 풀에서 제거할 때 최소한 유지해야 할 스레드 수
- 최대 스레드 수: 스레드 풀에서 관리하는 최대 스레드 수
newCachedThreadPool() 메소드는 1개 이상의 스레드가 추가되었을 경우 60초 동안 스레드가 아무 작업하지 않으면 해당 스레드를 풀에서 쫓아내는데, newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) 메소드는 스레드가 놀고 있어도 제재를 가하지 않는다.
// newCachedThreadPool()
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// newCachedThreadPool(int nThreads)
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
};
// 커스텀
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3, // 코어 스레드 개수
100, // 최대 스레드 개수
120L, // 최대 놀 수 있는 시간 (이 시간 넘으면 스레드 풀에서 쫓겨 남.)
TimeUnit.SECONDS, // 놀 수 있는 시간 단위
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>() // 작업 큐
);
스레드 풀 종료
- 기본적으로 스레드 풀의 스레드는 데몬 스레드가 아니므로 main 스레드가 종료되더라도 프로세스는 계속 실행 중이다.
- 따라서 main 스레드가 종료되면 해당 스레드 풀을 종료해야 한다.
메소드 종류
- shutdown()
- void 리턴 타입
- 현재 처리 중인 작업 뿐만 아니라 작업 큐에 대기하고 있는 모든 작업을 처리한 뒤에 스레드 풀을 종료한다.
- shutdownNow()
- List 리턴 타입
- 현재 작업 처리 중인 스레드를 interrupt해서 작업 중지를 시도하고 스레드 풀을 종료한다.
- 리턴 값은 작업 큐에 있는 미처리된 작업의 목록이다.
- awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- boolean 리턴 타입
shutdown()메소드 호출 이후, 모든 작업 처리를 timeout 시간 내에 완료하면 true를 리턴하고, 그렇지 않으면 작업 처리 중인 스레드를 interrupt하고 false를 리턴한다.
작업 생성과 처리 요청
작업 생성
- 작업은 Runnable 또는 Callable 구현 클래스로 표현한다.
- 전자는 작업 완료 이후 리턴 값이 없지만, 후자는 리턴 값이 존재한다.
// Runnable
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 스레드가 처리할 내용
}
}
// Callable
Callable<T> task = new Callable<T>() {
@Override
public T call() throws Exception {
// 스레드가 처리할 내용
return T;
}
}
작업 처리 요청
- ExecutorService의 작업 큐에 Runnable 또는 Callable 객체를 넣는 행위를 말한다.
- 작업 처리 요청을 위해 ExecutorService는 2가지 메소드를 제공한다.
- execute(Runnable command)
- void 리턴 타입
- Runnable을 작업 큐에 저장하고, 작업 처리 결과를 받지 못함
- 예외가 발생하면 해당 스레드를 스레드 풀에서 제거함
- submit(Runnable task), submit(Runnable task, V result), submit(Callable task)
- Future 리턴 타입
- Runnable 또는 Callable을 작업 큐에 저장
- 리턴된 Future를 통해 작업 처리 결과를 알 수 있음
- 예외가 발생하더라도 스레드는 종료되지 않고 다른 작업에 재사용될 수 있음
- 가급적 이 메소드를 사용하는 것을 추천
- execute(Runnable command)
execute() 메소드로 작업 처리 요청한 경우
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Runnable runnable = () -> {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) executorService;
int poolSize = threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize();
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("[총 스레드 개수: " + poolSize + "] 작업 스레드 이름: " + threadName);
int value = Integer.parseInt("삼");
};
executorService.execute(runnable);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
최대 스레드 개수가 2개인 스레드 풀을 생성한 다음 10개의 작업을 요청해 보자. 이때 각 작업에는 고의로 예외가 발생하는 코드를 집어 넣었다. 그리고 실행하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나온다.
[총 스레드 개수: 1] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "삼"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:652)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:770)
at practice.Main.lambda$main$0(Main.java:18)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1128)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:628)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-3
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-3" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "삼"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:652)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:770)
at practice.Main.lambda$main$0(Main.java:18)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1128)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:628)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-2" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "삼"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:652)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:770)
at practice.Main.lambda$main$0(Main.java:18)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1128)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:628)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)
분량 상 3개의 출력문만 가져와 보았다. 스레드 풀의 스레드 최대 개수 2는 변함이 없지만, 실행 스레드의 이름을 보면 모두 다른 스레드가 작업을 처리하고 있다. 이것은 작업 처리 도중 예외가 발생하면 해당 스레드를 스레드 풀에서 제거하고, 새 스레드를 생성해서 넣기 때문이다.
submit() 메소드로 작업 처리 요청한 경우
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Runnable runnable = () -> {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) executorService;
int poolSize = threadPoolExecutor.getPoolSize();
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("[총 스레드 개수: " + poolSize + "] 작업 스레드 이름: " + threadName);
int value = Integer.parseInt("삼");
};
executorService.submit(runnable);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
결과는 다음과 같다.
[총 스레드 개수: 1] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-1
[총 스레드 개수: 2] 작업 스레드 이름: pool-1-thread-2
예외가 발생하더라도 기존 스레드를 재활용하여 작업을 처리하는 것을 알 수 있다.
블로킹 방식의 작업 완료 통보
submit()메소드는 매개 값으로 넘긴 Runnable 또는 Callable 작업을 스레드 풀의 작업 큐에 저장하고 즉시 Future 객체를 리턴한다.- Future 객체는 작업이 완료될 때까지 기다렸다가 최종 결과를 얻는데 사용된다.
- Future 객체는 이름에서 알 수 있듯이 작업 결과를 나타내지 않는다.
- 그래서 Future를 지연 완료 객체라고 부른다.
- Future의
get()메소드를 호출하면 스레드가 작업을 완료할 때까지 블로킹되었다가 작업을 완료하면 처리 결과를 리턴한다. - Future를 이용한 블로킹 방식의 작업 완료 통보에서 주의할 점은 작업을 처리하는 스레드가 작업을 완료하기 전까지는
get()메소드가 블로킹되므로 다른 코드를 실행할 수 없다.- 만약 UI를 변경하고 이벤트를 처리하는 스레드가
get()메소드를 호출하면 작업을 완료하기 전까지 UI를 변경할 수 없다. - 그래서
get()메소드를 호출하는 스레드는 별도의 스레드여야 한다. (새로운 스레드를 만들거나, 스레드 풀의 스레드에게 작업을 요청)
- 만약 UI를 변경하고 이벤트를 처리하는 스레드가
리턴 값이 없는 작업 완료 통보
- Runnable 객체로 작업을 생성
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
System.out.println("작업 처리 요청");
Runnable runnable = () -> {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("[처리 결과] " + sum);
};
Future<?> future = executorService.submit(runnable);
try {
future.get();
System.out.println("작업 처리 완료");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[실행 예외 발생함] " + e.getMessage());
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
위 예제는 리턴 값이 없고 단순히 1부터 10까지의 합을 출력하는 작업을 Runnable 객체로 생성하고, 스레드 풀의 스레드가 처리하도록 요청하였다.
작업 처리 요청
[처리 결과] 55
작업 처리 완료
리턴 값이 있는 작업 완료 통보
- Callable 객체로 작업을 생성
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
System.out.println("작업 처리 요청");
Callable<Integer> task = () -> {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
};
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(task);
try {
int sum = future.get();
System.out.println("[처리 결과] " + sum);
System.out.println("작업 처리 완료");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[실행 예외 발생함] " + e.getMessage());
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
위 예제는 1부터 10까지 더한 값을 리턴 값으로 설정하였다. 실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
작업 처리 요청
[처리 결과] 55
작업 처리 완료
작업 처리 결과를 외부 객체에 저장
- 스레드가 작업한 결과를 외부 객체에 저장해야 할 경우가 있다.
- ex) 두 개 이상의 스레드가 작업 처리를 완료하고 외부 Result 객체에 작업 결과를 저장하면, Result 공유 객체가 작업들을 취합하여 애플리케이션에게 알릴 수 있다. 그러면 애플리케이션은 해당 정보를 통해 어떤 작업을 처리할 수 있다.
public class Result {
int accumValue;
public synchronized void addValue(int value) {
this.accumValue += value;
}
}
public class Task implements Runnable {
private final Result result;
public Task(Result result) {
this.result = result;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result.addValue(sum);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
System.out.println("[작업 처리 요청]");
Result result = new Result();
Runnable task1 = new Task(result);
Runnable task2 = new Task(result);
Future<Result> future1 = executorService.submit(task1, result);
Future<Result> future2 = executorService.submit(task2, result);
try {
result = future1.get();
result = future2.get();
System.out.println("[처리 결과] " + result.accumValue);
System.out.println("[작업 처리 완료]");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("[실행 예외 발생함] " + e.getMessage());
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
submit(Runnable task, V result)메소드를 사용하면 2번째 인자를 반환 받을 수 있다. 즉, 위 예제에서는 Result 객체를 집어 넣고 작업을 하면서 Result의 상태를 바꾸면 되는 것이다.- 실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
[작업 처리 요청]
[처리 결과] 110
[작업 처리 완료]
작업 완료 순으로 통보
- 작업의 양과 스레드 스케줄링에 따라서 작업을 빨리 요청한다고 해서 가장 빠르게 완료되지 않을 수 있다.
- 만약 여러 개의 작업이 순차적으로 처리될 필요 없고, 처리 결과도 꼭 순차적으로 이용할 필요가 없다면 작업 처리가 완료된 것부터 결과를 얻어 이용하면 된다.
- CompletionService의
poll()메소드 또는take()메소드를 사용한다.poll(): 완료된 작업의 Future를 가져오되, 완료된 작업이 하나도 없다면 null을 리턴take(): 완료된 작업의 Future를 가져오되, 완료된 작업이 없다면 블로킹
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
CompletionService<Integer> completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executorService);
System.out.println("[작업 처리 요청]");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
completionService.submit(() -> {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) {
sum += j;
}
return sum;
});
}
System.out.println("[처리 완료된 작업 확인]");
executorService.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
Future<Integer> future = completionService.take();
int value = future.get();
System.out.println("[처리 결과] " + value);
} catch (Exception e) {
break;
}
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
}
위 예제는 3개의 Callable 작업을 처리 요청하고 처리가 완료되는 순으로 작업의 결과 값을 출력하도록 하였다.
Future<Integer> future = completionService.take();
int value = future.get();
특히 위 코드는 completionService.take() 메소드가 완료된 작업이 있을 때까지 블로킹하므로 다음 줄의 future.get() 은 블로킹 없이 곧 바로 리턴된다.
콜백 방식의 작업 완료 통보
- 콜백이란 애플리케이션이 스레드에게 작업 처리를 요청한 후, 스레드가 작업을 완료하면 특정 메소드를 자동 실행하는 기법이다.
- 이때 자동 실행되는 메소드를 콜백 메소드라고 한다.
블로킹 방식 vs 콜백 방식
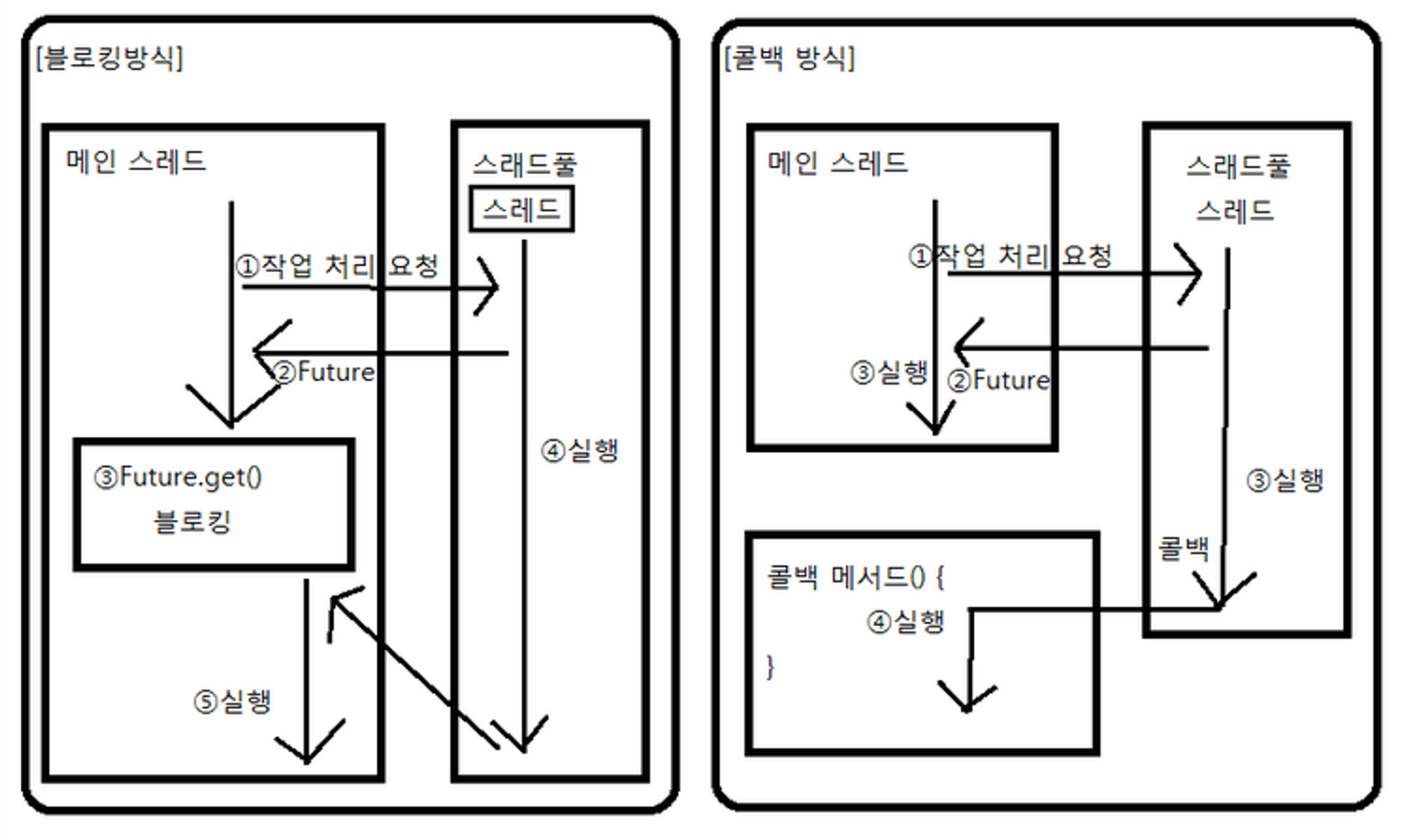
- 블로킹 방식은 작업 처리를 요청한 후 작업이 완료될 때까지 블로킹되지만, 콜백 방식은 작업 처리를 요청한 후 결과를 기다릴 필요 없이 다른 기능을 수행할 수 있다.
- 콜백 방식은 작업 처리가 완료되면 자동적으로 콜백 메소드가 실행되어 결과를 알 수 있기 때문이다.
콜백 방식 구현
- ExecutorService는 콜백을 위한 기능은 없고, Runnable 구현 클래스를 작성할 때 콜백 기능을 구현할 수 있다.
- 직접 정의하는 방식과 CompletionHandler를 이용하는 방식이 있다. 이번 포스팅에서는 후자의 방식만 살펴 본다.
CompletionHandler<V, A> callback = new CompletionHandler<>() {
@Override
public void completed(V result, A attachment) {}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, A attachment) {}
};
completed()메소드는 작업을 정상 처리 완료했을 때 호출되는 콜백 메소드이고,failed()메소드는 작업 처리 도중 예외가 발생했을 때 호출되는 콜백 메소드이다.- CompletionHandler에서 V는 결과 값의 타입이고, A는 첨부 값이다.
- 첨부 값은 콜백 메소드에 결과 값 이외에 추가적으로 전달하는 객체이다. 필요없다면 Void 타입으로 선언한다.
예제
public class CallbackExample {
private final ExecutorService executorService;
private CompletionHandler<Integer, Void> callback = new CompletionHandler<Integer, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Void attachment) {
System.out.println("completed() 실행: " + result);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
System.out.println("failed() 실행: " + exc.toString());
}
};
public CallbackExample() {
this(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
));
}
public CallbackExample(ExecutorService executorService) {
this.executorService = executorService;
}
public void doWork(String x, String y) {
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
int intX = Integer.parseInt(x);
int intY = Integer.parseInt(y);
int result = intX + intY;
callback.completed(result, null);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
callback.failed(e, null);
}
};
executorService.submit(task);
}
public void finish() {
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
두 문자열을 받아서 정수로 변환한 후 덧셈 연산을 하는 doWork() 메소드가 있다. 이때 콜백 방식으로 작동되며, 작업이 정상 처리되면 completed() 메소드를 호출하고, 그렇지 않으면 failed() 메소드를 호출하는 것을 알 수 있다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CallbackExample example = new CallbackExample();
example.doWork("3", "3");
example.doWork("3", "삼");
System.out.println("메인 스레드 작업 할당 완료");
example.finish();
}
}
메인 스레드에서는 두 번의 작업 할당을 하고, 출력문을 출력한 뒤 스레드 풀을 종료하는 신호를 보낸다.
메인 스레드 작업 할당 완료
completed() 실행: 6
failed() 실행: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "삼"
콜백 방식은 블로킹되지 않으므로 메인 스레드가 자신의 일을 쭉 실행할 수 있으므로 출력문이 먼저 나오고, 이후에 작업이 완료되는 대로 콜백 메소드가 실행된다. 첫 번째 doWork() 는 정상 종료이므로 잘 덧셈이 되고, 두 번째 doWork() 는 에러가 발생했으므로 에러 관련 콜백 메소드가 호출이 되어 무슨 에러인지 알려준다.
출처
이것이 자바다
예상 면접 질문 및 답변
스레드 풀이란?
스레드 풀은 작업 처리에 사용되는 스레드를 제한된 개수만큼 정해 놓고, 작업 큐에 들어오는 작업들을 하나씩 스레드가 맡아 처리하는 기법이다.
스레드 풀을 왜 사용하는가?
- 병렬 작업 처리가 많아지면 스레드 개수가 중가되고, 그에 따른 스레드 생성과 스케줄링으로 인해 CPU가 바빠져 메모리 사용량이 늘어난다. 이는 애플리케이션의 성능 저하로 이어진다.
- 스레드 풀은 작업 처리에 사용되는 스레드를 제한된 개수만큼 정해 놓고, 작업 큐에 들어오는 작업들을 하나씩 스레드가 맡아 처리한다.
- 작업 처리가 끝난 스레드는 다시 작업 큐에서 새로운 작업을 가져와 처리한다.
- 따라서 작업 처리 요청이 폭증해도 작업 큐라는 곳에 작업이 대기하다가 여유가 있는 스레드가 그것을 처리하므로 스레드의 전체 개수는 일정하며 애플리케이션의 성능도 저하되지 않는다.
블로킹 방식과 콜백 방식의 차이를 설명하라.
블로킹 방식은 작업 처리를 요청한 후 작업이 완료될 때까지 블로킹되지만, 콜백 방식은 작업 처리를 요청한 후 결과를 기다릴 필요 없이 다른 기능을 수행할 수 있다.
'스터디 > Java 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] volatile 키워드란? (0) | 2021.12.29 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Java의 동시성 이슈 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| [Java] Thread 문법 총 정리 (0) | 2021.12.19 |
| [Java] 오버로딩과 오버라이딩 (0) | 2021.12.15 |
| [Java] 동일성(identity)과 동등성(equality) (1) | 2021.12.12 |


댓글